The Red Sea: From Ancient Civilizations to Modern Marvels
Table of Content
The History of the Red Sea
The Red Sea Dimensions and Marine Life
The Red Sea as a Travel Destination
The Red Sea: From Ancient Civilizations to Modern Marvels
The Red Sea, a vital and historic waterway, is a treasure trove of natural beauty, rich history, and diverse marine life. Positioned between Africa and Asia, connected through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait and the Gulf of Aden in the south.
To the north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez, which leads to the strategic Suez Canal. The Red Sea Facts highlight its significance from ancient civilizations to modern conflicts, shaping the history and culture of the surrounding regions.
Today, it stands as one of Egypt's premier travel destinations, offering stunning landscapes, vibrant marine ecosystems, and a unique blend of historical sites and modern attractions.

The History of the Red Sea
Archeological History

The Red Sea has been a critical maritime route for millennia, with evidence of ancient trade routes and early civilizations utilizing its waters. Archeological finds reveal connections with Egypt, Mesopotamia, and the Arabian Peninsula, highlighting its importance in early commerce and exploration. The Red Sea History is deeply intertwined with the ambitions of ancient Egyptians, who were among the first to explore its waters. As early as 2500 BC, expeditions were launched to establish commercial routes to the Land of Punt, a region rich in resources such as gold, incense, and exotic animals.
Biblical History

The Parting of the Red Sea
The Red Sea is most famously associated with the biblical story of the Exodus, where Moses, under God's command, miraculously parted the waters to lead the Israelites out of Egyptian bondage. This momentous event, described in Exodus 14:21-22, is a cornerstone of Judeo-Christian tradition and symbolizes God's deliverance and protection of His chosen people. The exact location where Moses parted the sea is debated, with some scholars suggesting it may have been a marshy area near the northern end of the Red Sea or possibly a body of water known as the "Sea of Reeds."
Moses and the Ten Commandments on Mount Sinai
After the Israelites crossed the Red Sea, they journeyed through the wilderness and eventually reached Mount Sinai. It was on this sacred mountain, also known as Moses Mountain in the Sinai Peninsula, where Moses received the Ten Commandments from God. This event, detailed in Exodus 19-20, is another pivotal moment in biblical history. It established the moral and legal foundation for the Israelites and deeply influenced the religious traditions of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam.
Joshua's Recounting of the Red Sea Crossing
The significance of the Red Sea crossing is further emphasized in the Book of Joshua. In Joshua 24:6-7, Joshua, Moses' successor, recounts how God delivered the Israelites by parting the Red Sea, allowing them to escape the pursuing Egyptian army. This recounting serves as a reminder of God's power and faithfulness, reinforcing the importance of the Exodus in the collective memory of the Israelites.
The Israelites' Journey by the Way of the Red Sea
The Red Sea continued to play a role in the Israelites' journey even after the initial crossing. According to Numbers 21:4, the Israelites journeyed from Mount Hor by the Red Sea as they navigated the wilderness to avoid the land of Edom. This route underscored the challenges and trials faced by the Israelites during their 40 years of wandering before finally entering the Promised Land.
Secular History

Beyond religious texts, the Red Sea has been a crucial commercial and strategic waterway. Various empires and nations have recognized its significance, and control over its waters is often seen as key to regional dominance.
Pharaonic Era

During the Pharaonic period, the Red Sea served as a vital gateway for trade expeditions, particularly to the land of Punt, a region renowned for its wealth of resources like gold, myrrh, and exotic animals. The Red Sea History records some of the earliest known explorations conducted by the ancient Egyptians.
One of the most famous expeditions occurred around 1500 BC under the reign of Queen Hatshepsut, who sent a fleet down the Red Sea to Punt. These voyages were monumental, involving long, challenging journeys that not only facilitated trade but also fostered cultural exchanges. The Egyptians built early ports along the Red Sea coast, turning it into a hub of commerce and interaction between different civilizations, which played a crucial role in the prosperity and expansion of the Egyptian empire during the Pharaonic era.
Ptolemaic Era

Under the Ptolemies, the Red Sea became a bustling hub of commerce, connecting Egypt with the Indian subcontinent and beyond. The Ptolemies, keen on expanding Egypt's influence and wealth, established new ports along the Red Sea, such as Berenice and Myos Hormos, which became vital centers for maritime trade. These ports facilitated the exchange of goods like spices, textiles, and precious stones, significantly boosting Egypt's economy.
Alexander the Great and the Expansion of Red Sea Trade
In the late 4th century BC, Alexander the Great, the founder of the Ptolemaic dynasty, initiated Greek naval expeditions down the Red Sea towards the Indian Ocean, further enhancing the region's strategic importance. Greek navigators, eager to explore these new routes, meticulously compiled data on the Red Sea's geography and trade routes.
Agatharchides and the Documentation of Red Sea Maritime Routes
One of the most notable contributions from this era was the work of Agatharchides in the 2nd century BC, who gathered extensive information about the Red Sea. This knowledge culminated in the "Periplus of the Erythraean Sea," a detailed guide written by an unknown author around the 1st century. The Periplus not only provided a comprehensive description of the Red Sea's ports and sea routes but also documented how Hippalus discovered the monsoon winds, allowing for a direct route from the Red Sea to India. These advancements were crucial in shaping The Red Sea Map of ancient trade routes, marking the Ptolemaic Era as a period of significant maritime and commercial development.
Roman Era

The Romans capitalized on the Red Sea's strategic location, using it as a crucial corridor for transporting goods between Europe, Africa, and Asia. With the reign of Augustus, when the Roman Empire gained control over the Mediterranean, Egypt, and the northern Red Sea, the importance of this waterway in the empire’s vast trade network grew significantly.
The Red Sea History during this period highlights how Roman trade with India flourished, as goods from Indian ports, including those from China, were introduced to the Roman world via the Red Sea. The volume of traffic along this route increased under Roman rule, leading to the fortification of ports and the securing of maritime routes to protect this vital commercial artery.
Contact between Rome and China, although indirect, relied heavily on the Red Sea as a connecting route. However, by the 3rd century AD, the Aksumite Empire disrupted this trade network, affecting the flow of goods between these distant civilizations.
Additionally, from antiquity until the 20th century, the Red Sea also served as a route for the Red Sea slave trade, transporting slaves from Africa to the Middle East. These developments underscore the Red Sea’s enduring significance in global trade and its role in connecting diverse cultures across continents.
Islamic Era

During the Islamic Golden Age, the Red Sea was not only an essential route for pilgrims traveling to Mecca but also a thriving center for Islamic maritime trade. This vital waterway linked the Arab world with Africa and Asia, fostering significant cultural and economic exchanges. The Red Sea History during this era highlights its role in the spice trade, a key component of the global economy in the Middle Ages. The Red Sea served as a major artery for the transport of valuable spices from Asia to the Arab world and beyond.
In 1183, the Red Sea became the focus of a bold and controversial raid by Raynald of Châtillon, a Crusader lord who launched an attack on Muslim pilgrim convoys heading to Mecca. This audacious move stirred fury throughout the Muslim world, as there were fears that Raynald's fleet might sack the holy cities of Mecca and Medina. Although it appears that Raynald’s actual target was the lightly armed pilgrim convoys rather than the well-guarded cities themselves, the mere proximity of his raid to these sacred locations caused widespread alarm. This incident underscores the strategic importance of the Red Sea during the Islamic Era, not only as a trade route but also as a religious and political flashpoint.
The enduring significance of the Red Sea in Islamic history is evident in its continued use for both pilgrimage and trade, as well as its role in shaping the interactions between different cultures and civilizations across the region.
Modern Era
1513: The Portuguese Explorer Afonso de Albuquerque
In 1513, the Portuguese explorer Afonso de Albuquerque attempted to secure the Red Sea as a vital channel for Portugal by laying siege to Aden. Although forced to retreat, his fleet became the first from Europe in modern times to navigate the Red Sea, marking a significant moment in The Red Sea History.
1798: Napoleon's Campaign in Egypt
In 1798, Napoleon Bonaparte was ordered by France to invade Egypt and take control of the Red Sea. While the military campaign ultimately failed, it sparked renewed interest in connecting the Mediterranean with the Red Sea. Engineer Jean-Baptiste Lepère, who accompanied Napoleon, revitalized the ancient idea of building a canal—a vision that eventually led to the creation of the Suez Canal, which opened in 1869.
After World War II: United States and Soviet Influence
After World War II, the strategic importance of the Red Sea increased as the United States and the Soviet Union sought to exert their influence in the region. The growing volume of oil tanker traffic further underscored the Red Sea’s significance. However, the Six-Day War in 1967 led to the closure of the Suez Canal, disrupting global shipping until its reopening in 1975.
2023-2024: Yemeni Houthis and the Israel-Hamas War
More recently, during the 2023-2024 Israel-Hamas war, the Red Sea has been the site of increased tensions. Iranian-backed Yemeni Houthis have attacked Western ships, including warships, further complicating the security situation in this critical maritime route. These incidents highlight the ongoing volatility and strategic importance of the Red Sea in contemporary geopolitics.
The Red Sea Dimensions and Marine Life

Red Sea Dimensions, Depth, and Oceanography

The Red Sea stretches over 2,250 km in length, with a maximum width of 355 km, and depths reaching up to 2,211 meters. Covering a surface area of approximately 438,000 km², it is one of the world's most significant bodies of water. The Red Sea Dimensions vary considerably, with an average depth of 490 meters, though it plunges to a staggering 3,040 meters in the central Suakin Trough, making it a fascinating area for oceanographic studies.
Despite these depths, around 40% of the Red Sea is relatively shallow, with depths of less than 100 meters, and 25% of the sea is even shallower, at less than 50 meters deep. These extensive shallow shelves are rich in marine life and are home to over 1,000 invertebrate species and 200 types of soft and hard coral. The Red Sea, as the world's northernmost tropical sea, has been recognized as a Global 200 ecoregion, highlighting its importance and uniqueness in the global marine ecosystem. This combination of depth, biodiversity, and unique underwater topography makes the Red Sea a vital subject of study and a treasure trove of natural wonders.
The Climate of the Red Sea
The Red Sea Climate is shaped by two distinct monsoon seasons: the northeasterly monsoon and the southwesterly monsoon. These monsoon winds are caused by differential heating between the land and the sea, contributing to the Red Sea's unique weather patterns. The sea enjoys warm temperatures year-round, with surface water temperatures ranging from 22°C in winter to 29°C in summer. This consistent warmth supports the region's vibrant marine ecosystem, making it an ideal destination for diving and snorkeling.
The Red Sea is also characterized by very high surface temperatures and salinity levels, making it one of the warmest and saltiest bodies of seawater in the world. During the summer, the average surface water temperature can reach around 26°C (79°F) in the north and up to 30°C (86°F) in the south, with only a slight variation of about 2°C during the winter months. The overall average water temperature remains at a comfortable 22°C (72°F), with excellent temperature stability and visibility down to around 200 meters (660 feet). However, the Red Sea is also known for its strong winds and unpredictable local currents, adding an element of adventure to its otherwise serene waters. This unique combination of factors makes the Red Sea a fascinating and diverse marine environment, perfect for year-round exploration.
Marine Life and Animal Diversity and Ecosystem
Fish Species and Endemic Life
The Red Sea is home to an incredibly rich and diverse ecosystem, boasting over 1,200 species of fish, 10% of which are found nowhere else in the world. This high level of endemism makes The Red Sea Ecosystem particularly unique and valuable, contributing to its status as one of the world’s most biologically diverse marine environments.
Coral Reefs and Marine Habitats
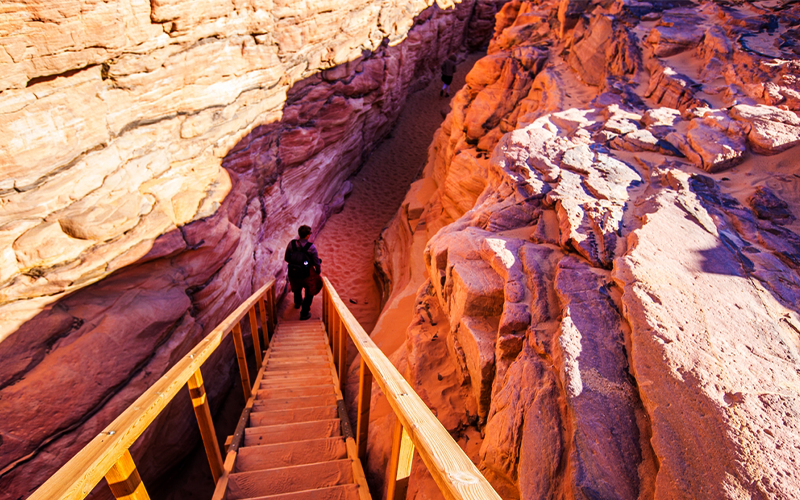
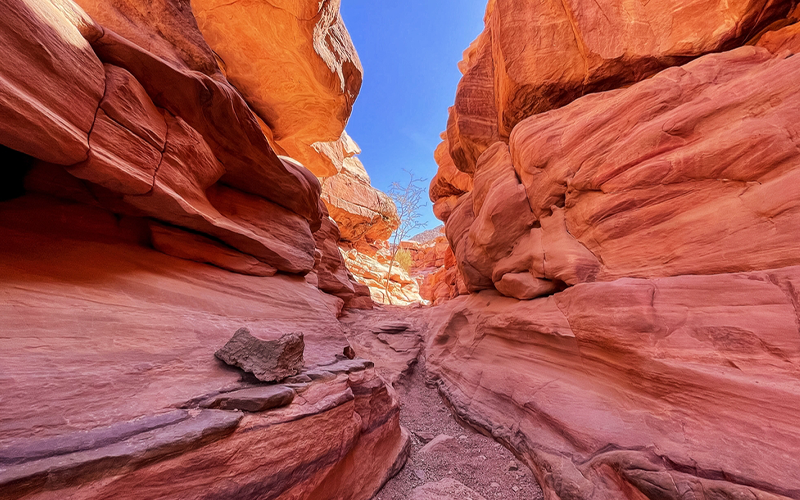
One of the key factors supporting this diversity is the extensive coral reef system that stretches over 2,000 km along the Red Sea’s coastline. These fringing reefs, which are between 5,000 and 7,000 years old, are primarily composed of stony acropora and porite corals. The reefs form platforms and lagoons along the coast, with some areas featuring unique formations like the famous Blue Hole at Dahab. In addition to the coastal reefs, the Red Sea hosts several offshore reefs, including true atolls. These unusual formations, which sometimes defy traditional coral reef classification, are largely attributed to the region’s high levels of tectonic activity.
Pelagic Species and Other Marine Life
Both the coastal and offshore reefs attract a wide variety of pelagic fish species, including 44 recorded species of sharks. The Red Sea is also home to over 175 species of nudibranchs, many of which are endemic to the region. Beyond the reefs, the Red Sea’s diverse habitats include seagrass beds, salt pans, mangroves, and salt marshes. Additionally, the deep Red Sea brine pools have been extensively studied for their unique microbial life, which is highly adapted to extreme environments.
Conservation and Marine Protection
Recognizing the high marine biodiversity of the Red Sea, the Egyptian government established the Ras Mohammed National Park in 1983. This protected area enforces strict regulations to safeguard the local marine life, making it a major draw for diving enthusiasts from around the world. While the majority of Red Sea species are harmless, some can be hazardous to humans, so divers are encouraged to exercise caution. The preservation of The Red Sea Ecosystem through such initiatives ensures that its rich biodiversity will continue to thrive for future generations to explore and enjoy.
The Red Sea as a Travel Destination
Famous Egyptian Tourist Destinations
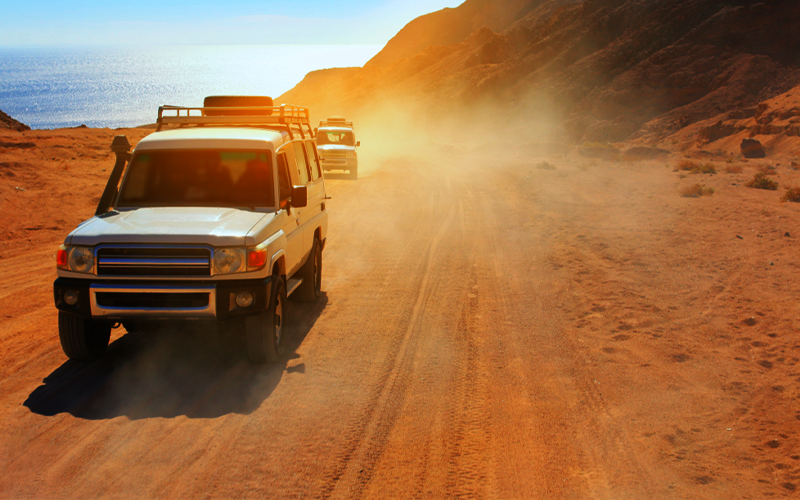
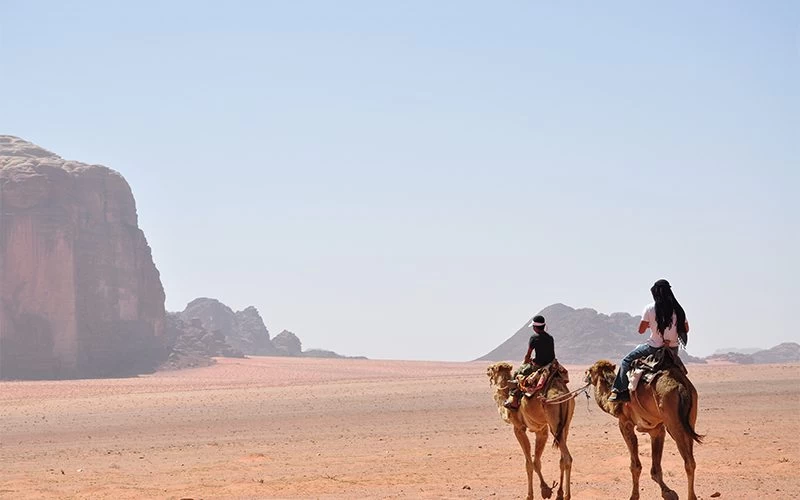
The Red Sea Tourist Destinations along the Egyptian coastline are renowned for their stunning beauty and world-class amenities, attracting visitors from all over the globe. Key tourist spots like Hurghada, Sharm El Sheikh, and Marsa Alam offer luxurious resorts, breathtaking views, and some of the best diving experiences in the world. These destinations are not only popular for their scenic beauty but also for their rich marine life and pristine coral reefs, making them a haven for divers and snorkelers alike.
Among the most famous diving sites are Ras Mohammed, known for its vibrant coral reefs and diverse marine life, and the SS Thistlegorm, a historic shipwreck that has become a must-see for underwater explorers. Other notable sites include Elphinstone Reef, The Brothers, Daedalus Reef, and St. John's Reef, each offering unique underwater landscapes and thrilling encounters with marine species.
The Red Sea's reputation as a premier diving destination was cemented in the 1950s by the pioneering expeditions of Hans Hass, and later by Jacques-Yves Cousteau, whose explorations brought global attention to the area's underwater wonders. Today, popular tourist resorts such as El Gouna, Hurghada, Safaga, and Marsa Alam on the west shore, and Sharm-el-Sheikh, Dahab, and Taba on the Egyptian side of the Sinai Peninsula, continue to draw travelers seeking both adventure and relaxation.
These resorts not only offer access to some of the world’s most spectacular diving sites but also provide a range of other activities and amenities, ensuring a well-rounded and unforgettable vacation experience on the shores of the Red Sea.
Water Sport Activities

Diving: Explore the Red Sea's Underwater Wonders
Diving is one of the most popular activities in the Red Sea, thanks to its stunning coral reefs and vibrant marine life. From the world-renowned dive sites of Sharm El Sheikh and Hurghada to hidden gems along the coastline, the Red Sea offers countless opportunities to explore underwater landscapes teeming with life. Divers can encounter unique species such as crocodile fish, turtles, and even dolphins, making each dive an unforgettable experience.
Snorkeling: Immerse Yourself in the Beauty of the Reefs
For those who prefer to stay closer to the surface, snorkeling offers a similarly rewarding experience, allowing you to immerse yourself in the beauty of the reefs without the need for scuba gear. The Red Sea's clear, warm waters make it an ideal destination for snorkeling, with vibrant coral formations and diverse marine life just below the surface.
Windsurfing: Glide Across the Waves with the Red Sea's Reliable Winds
The Red Sea is a hotspot for windsurfing, with its reliable winds and expansive open waters creating ideal conditions for this thrilling sport. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a beginner looking to learn, the Red Sea offers an exhilarating windsurfing experience.
Kitesurfing: Catch the Air and Ride the Waves
Kitesurfing in the Red Sea is an adventure like no other. The consistent winds and clear waters make it a perfect spot for kitesurfing enthusiasts to catch some air and ride the waves. Whether you’re gliding across the water or soaring above it, kitesurfing in the Red Sea is sure to provide an unforgettable experience.
Beach Relaxation: Unwind on Pristine Shores
After a day full of water sports, the Red Sea's pristine beaches offer the perfect setting for relaxation. Whether you’re at a bustling resort or a secluded coastal spot, the tranquil views and gentle sea breeze provide a peaceful escape, allowing you to unwind and soak in the beauty of the Red Sea.
Why do I book with Sun Pyramids Tours?
1) Expertise and Experience: Sun Pyramids Tours has 53 years of experience in the travel and tourism industry.
2) Customized Itineraries: Sun Pyramids Tours offers tailored itineraries to suit your preferences. Whether you're interested in historical sites, cultural immersion, or adventure activities, we can design a tour that matches your interests.
3) Local Connections and Insider Access: Sun Pyramids Tours can provide you with unique opportunities and insider access to attractions and experiences that may not be easily accessible to independent travelers.
4) Hassle-Free Planning: Sun Pyramids Tours can take the stress out of planning your trip. We handle all the logistics, including accommodations, transportation, and guided tours, at competitive prices… Relax and enjoy your vacation without worrying about the details.
5) Customer Satisfaction: Sun Pyramids Tours prides itself on providing excellent customer service and ensuring customer satisfaction. They strive to meet and exceed your expectations, making your trip enjoyable and memorable. Add trip advisor reviews, Facebook page reviews, etc.
6) Safety and Security: Sun Pyramids Tours prioritizes the safety and security of their guests. We work with trusted partners, adhere to safety guidelines, and provide support throughout your journey to ensure a safe and comfortable travel experience.
Egypt warmly welcomes visitors with its majestic Nile River, desert landscapes, and the fertile Delta, along with its remarkable and awe-inspiring landmarks. With our Egypt tour packages, you’ll have the chance to uncover the most mesmerizing wonders of the land of the Pharaohs, including the iconic Giza Pyramids, the Great Sphinx, Abu Simbel, the Karnak temples, and so much more. The Nile River is also the perfect setting for one of our Nile cruises, where you can sail through history, admiring the magnificent monuments between Luxor and Aswan. The opportunity is right here for you—don’t miss out, book with us today!
.DvizhAGb.gif)
Plan your next adventure now
Related Tours
Frequently Asked Questions
See more

There are no frequently asked questions :)
Related Blogs

Plan A Trip to Egypt
+1 more
Ultimate Guide: How To Plan A Trip To Egypt

Christmas and New Year in Egypt
+1 more
Christmas and New Year in Egypt

Egypt Hidden Gems
+1 more
Egypt Hidden Gems
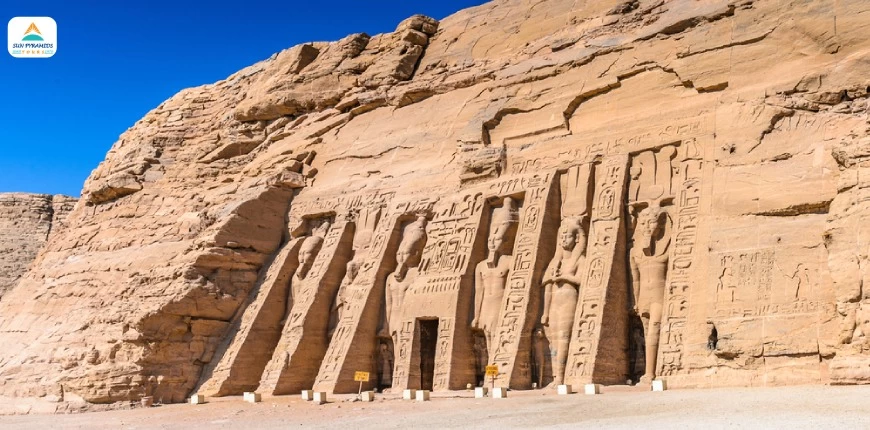

Abu Simbel Temple
+1 more
Abu Simbel Temple
Need help to Finding your Trip?
Offers
Make Trip
trips
Home







.webp)
.webp)















 2.jpg)
 1.jpg)



.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)










.webp)
.webp)









